

The value ~ means that the user will be limited to the personal folder (e.g /home/user12). to do this, find the DefaultRoot commented line and uncomment it. Now, we have to activate the DefaultRoot option. MaxInstances: The maximum number of simultaneous connections you want to allow on your FTP server. PassivePorts: Restricts the range of ports from which the server will select when sent the PASV command from a client. Almost all of the time this port is 21 and you should not have to change it unless you are blocked by a firewall. Port: The connection port to the FTP server. TimeoutIdle: The time, in seconds, after which a client is automatically disconnected if it is no longer active on the FTP server.ĭefaultRoot: Controls the default root directory assigned to a user upon login. This name will be displayed when clients connect to the server. ServerName: Specifies the name of the FTP server. # Use this directive to release that constrain. # Users require a valid shell listed in /etc/shells to login. # Use this to jail all users in their homes # If set on you can experience a longer connection delay in many cases. # Set off to disable IPv6 support which is annoying on IPv4 only boxes.
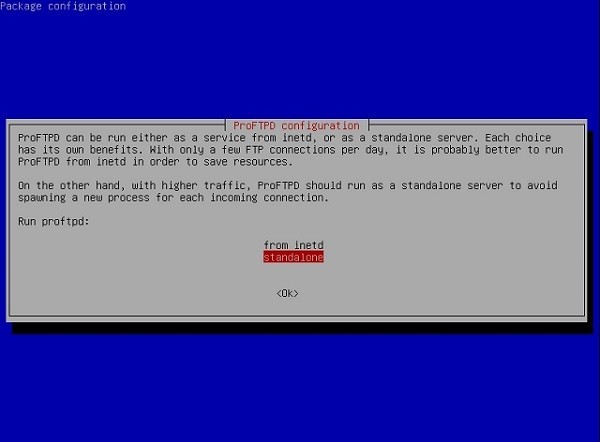
# To really apply changes, reload proftpd after modifications, if # /etc/proftpd/nf - This is a basic ProFTPD configuration file. The file will resemble the following text. sudo apt-get install proftpdĭuring installation, you will be asked if you want to install in inetd or standalone mode. PrerequisitesĪ newly deployed Vultr Debian or Ubuntu server instance. In this guide, we will see how to configure an FTP server (ProFTPd) to transfer files between your PC and your server.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
